Understanding Climate Change in Çankaya, Ankara: A Glimpse into the Future
- Çağrı Karaman
- Jan 13, 2025
- 3 min read
Climate change is no longer a distant threat but a reality reshaping communities worldwide. In Çankaya, a district of Ankara, Turkey, climate trends and projections highlight the urgency of understanding and addressing environmental shifts. Drawing insights from the recent Climate Change Adaptation Strategy and Action Plan (2024-2030), this blog delves into how global warming is impacting the region and what lies ahead.
An Overview of Çankaya’s Climate
Situated at an altitude of 850 to 1,200 meters, Çankaya features diverse topography, including flatlands and rolling hills. The district experiences a continental climate with annual average temperatures of 11.9°C and average annual precipitation of 393 mm. Seasonal extremes are evident, with frosty winters and hot summers. Historically, January has been the coldest month, averaging 0.2°C, while August peaks at 23.4°C.
However, recent decades have seen increasing variability and shifts in these patterns. The district is not immune to the global climate crisis, with projections indicating significant changes in temperature, precipitation, and weather extremes.
Key Climate Risks in Çankaya
The Action Plan identifies several pressing climate risks for Ankara, including:
Urban Flooding: Intensified by heavy rainfall and inadequate drainage systems.
Heatwaves: Amplified by urban heat islands, limited green spaces, and extensive use of heat-retaining materials.
Water Scarcity: Prolonged droughts jeopardize water supply security, as highlighted by the 2007-2008 drought.
Infrastructure Vulnerability: Extreme weather events threaten urban infrastructure.
Biodiversity Loss: Urban sprawl and climate change reduce natural habitats.
Projections for the Future
Using NASA’s NEX-GDDP-CMIP6 dataset, climate trends were analyzed under two scenarios: SSP245 (moderate mitigation) and SSP585 (high emissions). The findings reveal stark differences:
Temperature Trends
By the end of the century, annual average temperatures are projected to increase by 2-3°C under SSP245 and 5-6°C under SSP585.
Heatwaves and warm spells will become more frequent and prolonged, especially under SSP585.
Conversely, cold spells are expected to diminish, potentially disappearing entirely.
Precipitation Patterns
Annual precipitation is expected to remain relatively stable under SSP245 but show greater variability under SSP585.
Extreme precipitation events (e.g., maximum 1-day rainfall) are projected to increase, heightening flood risks.
Seasonal Shifts
Summer days and consecutive hot days will increase, exacerbating heat stress and energy demands.
Frost and cold days will decline sharply, altering agricultural and ecological processes.
Strategies for Adaptation
The report underscores the importance of proactive adaptation to mitigate these impacts. Key recommendations include:
Improving Water Management: Developing resilient water systems to address drought and variability.
Urban Planning: Enhancing green infrastructure to counteract urban heat islands.
Disaster Preparedness: Strengthening infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events.
Biodiversity Conservation: Protecting and restoring natural habitats to sustain local ecosystems.
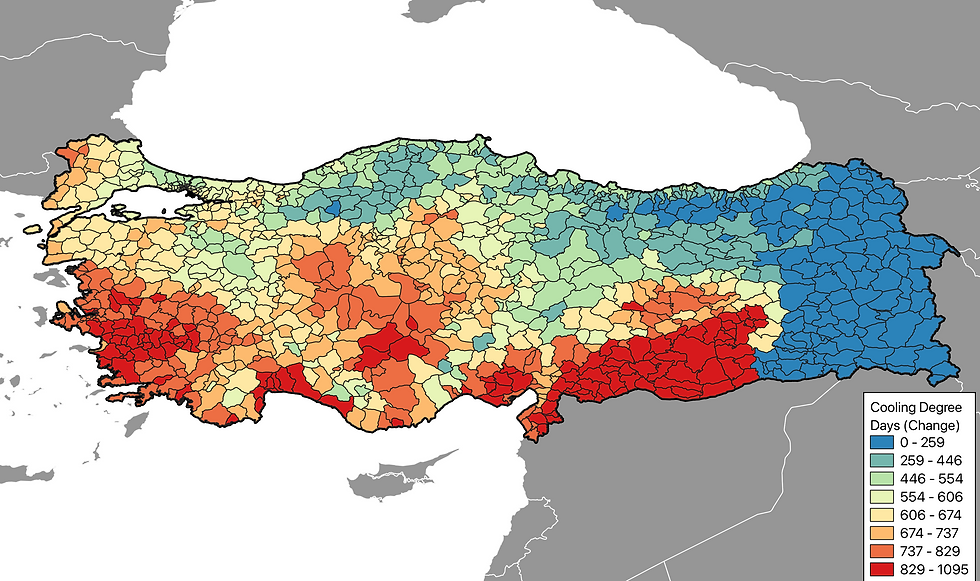
Visualizing the Change
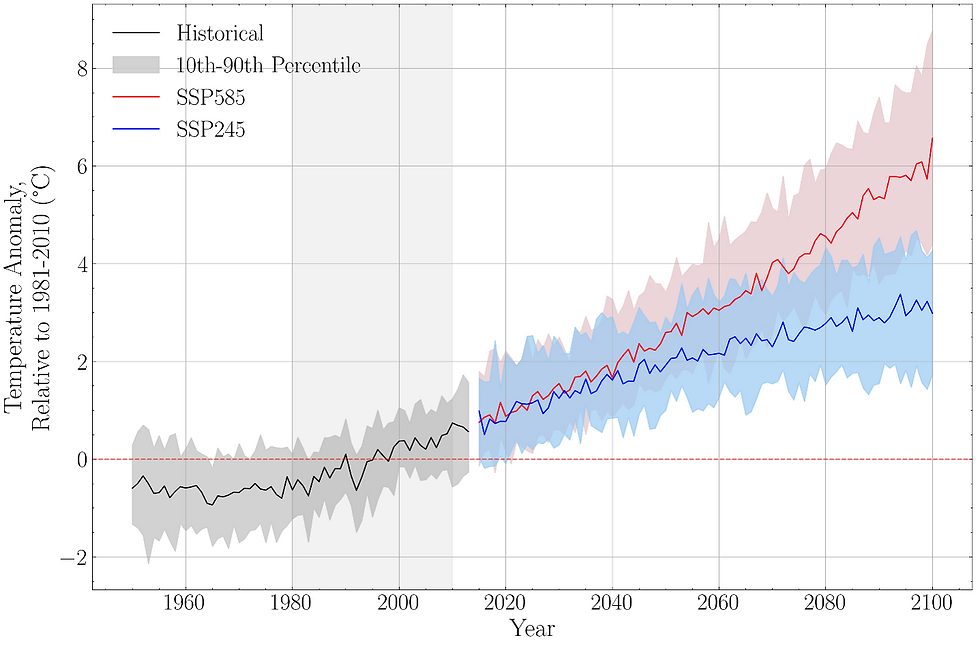
Figure 1: Average annual temperature anomalies for Çankaya under SSP245 and SSP585 scenarios relative to the 1981-2010 baseline. The shaded areas represent the range of model projections, with the black line indicating the median.
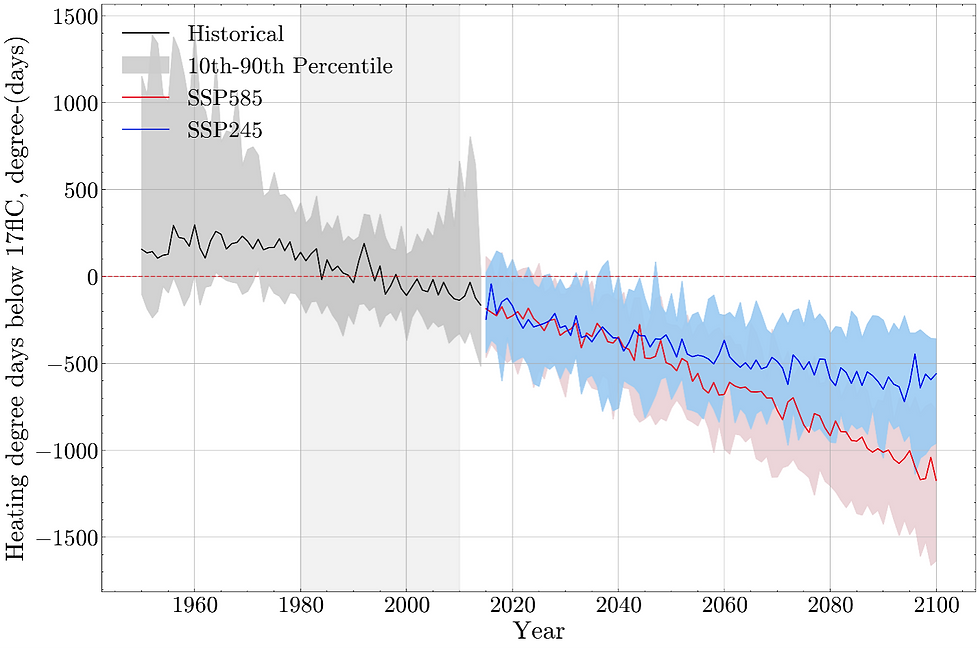
Figure 2: Average heating degree days anomalies for Çankaya under SSP245 and SSP585 scenarios relative to the 1981-2010 baseline. The shaded areas represent the range of model projections, with the black line indicating the median.
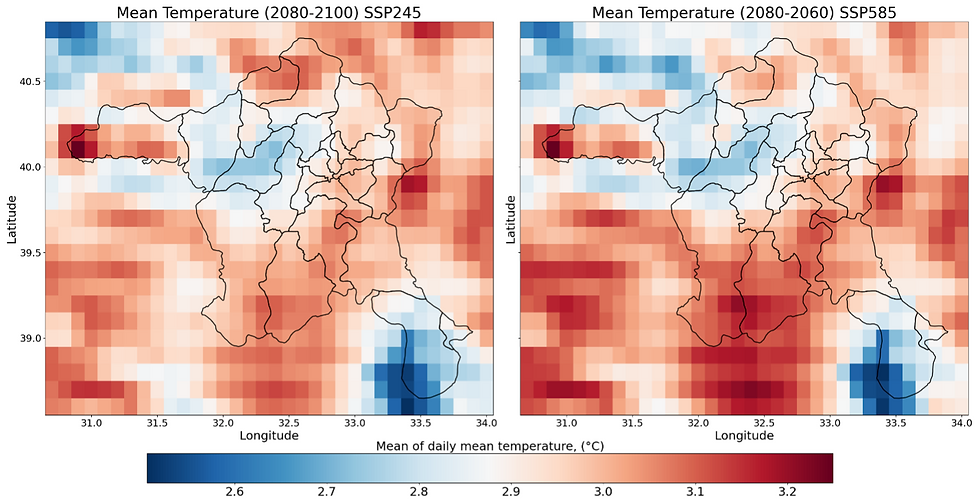
Figure 3: Average annual temperature anomalies (2060-2080) map for Çankaya under SSP245 and SSP585 scenarios relative to the 1981-2010 baseline.
Conclusion
Climate change poses profound challenges for Çankaya, impacting everything from water resources to public health and infrastructure. While mitigation efforts can reduce the severity of these changes, adaptation strategies are essential for building resilience. By understanding these trends and preparing for the future, Çankaya can lead the way in climate action and sustainable development.
Comments